Hyperbaric chambers are split into 2 categories, HBOT or mHBOT chamber. Although they seem similar, the technical differences and medical benefits between the two can be vast.
The main technical differences are given by the working pressure and the purity of the oxygen used in the therapy.
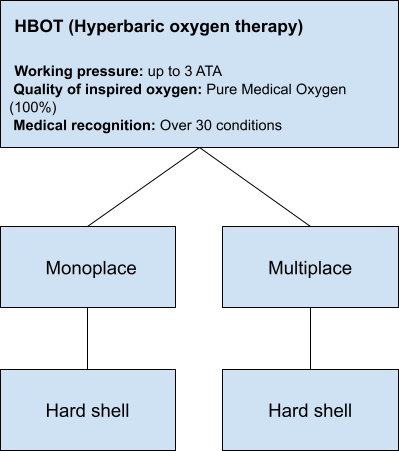
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) Chambers
HBOT chambers are classified as Class IIB medical devices, certified in compliance with CEE 93/42 standards. These chambers operate using 100% pure medical oxygen and can reach working pressures of up to 3 ATA. Constructed with durable hard shells, they are designed to accommodate anywhere from 1 to 30 individuals at a time.
Accreditation and Operational Requirements
- Regulatory Compliance: HBOT chambers must be accredited by the FDA.
- Qualified Personnel: Operation requires the presence of certified medical staff and regularly trained operators and a physician.
- Usage Restrictions: These chambers can only be used in authorized hospitals or medical clinics, and a medical clearance is mandatory for operation.
Key Features
- Working Pressure: Up to 3 ATA.
- Medical Oxygen: Utilizes 100% pure medical oxygen for therapy.
- Multi-Place Capabilities: Allows for medical interventions, including those in Intensive Care settings.
- Safety Systems: Equipped with advanced fire suppression systems (HSFS) and protection against voltage fluctuations or drops.
- Proven Efficacy: Supported by over 300 published medical studies.
- FDA Approval: Authorized for use in the treatment of 30 different conditions.
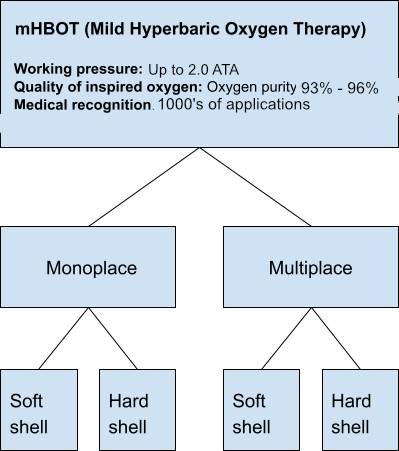
Mild Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (mHBOT) Chambers
mHBOT chambers are non-medical hyperbaric devices that come in both hard and soft-shell models, accommodating 2 to 6 individuals. Unlike medical HBOT chambers, mHBOT uses oxygen with lower purity of oxygen, generated by concentrators with oxygen levels ranging from 93% – 96%. These chambers typically operate up to 2.0 ATA.
Due to production costs up to 10 times lower than medical HBOT chambers, mHBOT chambers are electronic and have all the features of HBOT plus additional enhancements such as being able to bring a electronic device inside. They do not require medical authorization or the presence of trained medical personnel, as they are not classified as medical devices and are suitable for administering medical therapies.
Key Distinctions Between HBOT and mHBOT
mHBOT can achieve the same results as HBO but with longer durations. Such as 15+ more minutes to achieve oxygen saturation.
Safety Considerations in HBOT Chambers
HBOT chambers pose a significant fire risk due to the high concentration of pure oxygen. As a result, electronic or heat-emitting devices are strictly prohibited inside the chamber. According to the National Fire Protection Act (NFPA) chapter 14, standards, multi-place HBOT chambers must feature pneumatically activated fire suppression systems and an emergency access hatch for rapid intervention.
Treatment Efficacy and Duration
Treatment efficacy depends on several factors, including session duration, chamber pressure, and oxygen purity.
- mHBOT Chambers: Sessions typically last 60-90 minutes.
- HBOT Chambers: Sessions range from 120-150 minutes, with cumulative effects achieved over multiple sessions.
The recommended a working pressure of 2-3 ATA and oxygen purity exceeding 99.5% for effective treatment. In accredited HBOT medical centers, treatment plans are tailored by hyperbaric medicine specialists based on the patient’s condition.
Why Does Confusion Persist?
HBOT chambers provide a medical treatment. Whereas mHBOT is a therapy.
Adding to the confusion, some medical clinics opt for mHBOT chambers due to their lower cost, further blurring the distinction between these non-medical devices and certified HBOT chambers.
mHBOT is becoming widely used in the US because of it lower cost and convenience of being able to use electronic devices inside the chamber as the O2 purity in the chamber averages 28% and is not a fire risk.
This misleads the patient and sometimes doctors as to the real characteristics of the respective hyperbaric chamber, causing very long delays in the application of appropriate medical treatment, at key moments in the evolution of the disease.
Contributing to this confusion is the fact that certain medical clinics have decided to purchase such (non-medical) mHBOT devices for cost reasons, which are considerably cheaper than HBOT chambers.
Comparison of main features:
| HBOT Chamber | mHBOT Chamber |
|---|---|
| Maximum working pressure | |
| 3 ATA (tested up to 6 ATA) | 2.0 ATA |
| Quality of inspired oxygen | |
| Pure medical oxygen (100%) | Oxygen of purity 93% – 96% |
| Staff required | |
| At least one clinical specialist doctor with skills in hyperbaric medicine + At least 2 hyperbaric chamber operators, certified + Medical Assistant | mHBOT chambers do not require the presence of a certified operator or a medical professional |
| Wrapper type | |
| C-Steel hard shell, PED certified + Acryl PMMA, PVHO-1 and NFPA 99 certified | Can be hard or soft shell. There is no standard for material |
| Permission to operate | |
| HBOT chambers require medical authorization to operate | mHBOT chambers do not require medical authorization to operate |
| Classification | |
| Class IIB Medical Device | Not classified as a medical device |
| Fire extinguishing system | |
| The HBOT multi-location chambers have a high-performance fire-fog and water-extinguishing system (HSFS) | mHBOT chambers do not have fire extinguishing systems |
| Duration of therapy | |
| Most often between 120 – 150 minutes depending on the schedule | 60 – 90 minutes |
| Location/Location | |
| HBOT chambers can only be used in authorized hospitals or medical clinics for on-label use. | mHBOT are often used in clinics for off-label use. |
| Medical studies | |
| More than 300 published medical studies attesting to the effectiveness of treatment in HBOT chambers | 1000’s of published medical studies attesting to the effectiveness of treatment in HBOT chambers |
| Protection against voltage drops | |
| There must be a protection system against fluctuations or drops in electrical voltage | In mHBOT chambers there is no mandatory protection against voltage fluctuations or drops |
| Medical Recognition | |
| FDA approved for 14 different conditions, Air and gas bubbles in the blood, Anemia, Burns, Carbon monoxide poisoning, Crush injury, Decompression sickness, Gas gangrene, Hearing loss, Infection of the skin and bone, Radiation injury, Brain abscess, Arterial gas embolism, Central retinal artery occlusion, Chronic refractory osteomyelitis | Recommended by the FDA and the Underwater and Hyperbaric Medicine Society (UHMS) for a single condition: Alzheimer’s, Arthritis, Anti-Aging, Bone disorders, Cancer, Chronic viruses, Lyme disease, Parkinson’s’, Post Traumatic Stress, Traumatic Brain Injury and much more |
